1.What is Plasma?
Plasma is the fourth state of matter. We often think of matter in its normal state as: solid, liquid, and gas. In the normal state, water exists in three states: ice, water, and steam.
The difference between those states is related to the energy level. When additional energy in the form of heat is applied to ice, the ice melts and forms water. If energy continues to be added, the water continues to evaporate and form steam. If you add significant energy to the steam – heated to about 11,700°C – the steam will break up into several component gases, and will become conductive, or ionized. This high-energy ionized gas is called a plasma.
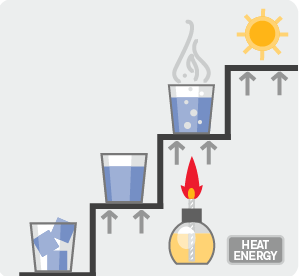
States of matter
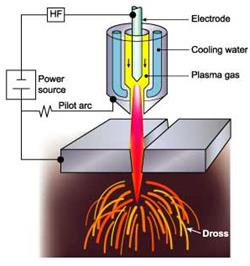
A plasma cutting system uses a plasma stream to transfer energy to a conductive work material. The plasma stream is usually formed by forcing a gas such as nitrogen, oxygen, argon – or even air (compressed air) – through a nozzle (nozzle). An electric current generated by an external power source adds enough energy to the gas stream to ionize it, turning it into a Plasma arc with a temperature of about 40,000˚ F. The plasma arc cuts the material by doing melt metal and blow away the molten metal.
2.Basic structure of a Plasma system
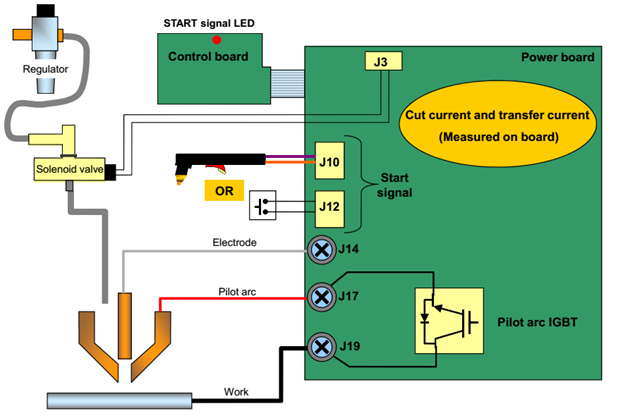
Supply: a constant DC power source. Open circuit voltage between 240 and 400 VDC. The output current (amperage) and power of the plasma cutting source will determine the cutting speed and cutting material thickness. The main function of the power supply is to provide energy for maintaining the plasma arc after -ionization.
The basic principle of creating a plasma arc
Initial arcing circuit (high voltage): in most torches 130A and above will be liquid cooled, this is a high frequency circuit that generates AC voltages of 5,000 to 10,000 Voltage at 2MHz. It is this voltage that creates a high-intensity arc inside the torch to ionize the gas, creating a plasma beam. Instead of using frequency arc priming technology as mentioned above, here it uses electrode moving technology, also known as "blowback start" to ionize the gas.
3.Application of Plasma
- Shipbuilding
- Shipping
- Energy
- Steel structure
- Pipeline
- Build
4. Compare the advantages of Plasma with Oxy-Gas: In terms of cutting speed:
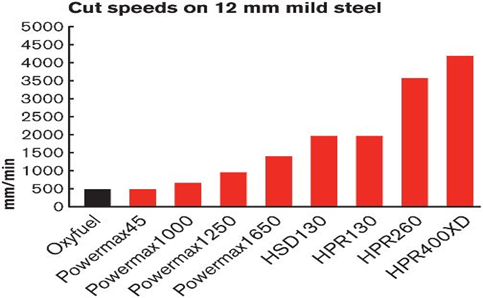
(Source Hypertherm)